Normalize¶
Raises (or lowers) the loudest peak of the audio track to a given volume. This process is called audio normalization.
Note that Normalize performs peak normalization (used to prevent audio clipping) and not loudness normalization.
Syntax and Parameters¶
Normalize (clip, float "volume", bool "show")
- clip
- Source clip. Supported audio sample types: 16-bit integer and 32-bit float.Other sample types (8, 24 and 32-bit integer) are automatically converted to 32-bit float.
- volume
Set the amplitude of the loudest audio. Default = 1.0 for peaking at 0dB: for floating-point samples, this corresponds to the range -1.0 to +1.0, and for 16-bit integer samples, this corresponds to the range -32768 to +32767 – the widest range possible without clipping.
For a particular peak decibel level, use the equation
volume= 10 dB / 20For example, set a -3dB peak with
volume= 10-3/20 or 0.7079.Where multiple audio channels are present, all channel gains are set in proportion. For example, if the loudest peak on the loudest channel comes to -10dB, by default a gain of +10dB is applied to all channels.
Default: 1.0
- show
If true, a text overlay will show the calculated amplification factor and the frame number of the loudest peak.
Default: false
Normalization and Floating-point Audio¶
The idea of digital clipping (when the signal is outside the range that can be stored accurately) really applies only to integer sample types; floating-point samples will never become clipped in practice, as the maximum value is around 3.4×1038 – some 29 orders of magnitude (580 dB) larger than 16-bit samples can store.
Normalize is therefore not needed for floating-point audio, but using it is recommended before converting to an integer type, especially if any processing has been done – such as amplification, mixing or equalization – which may expand the audio peaks beyond the integer clipping range.
Examples¶
Normalize signal to 98%
video = AviSource("video.avi")
audio = WavSource("audio.wav").Normalize(0.98)
return AudioDub(video, audio)
Normalize each channel separately (eg for separate language tracks):
video = AviSource("video.avi")
audio = WavSource("audio2ch.wav")
left_ch = GetChannel(audio,1).Normalize()
right_ch = GetChannel(audio,2).Normalize()
return AudioDub(video, MergeChannels(left_ch, right_ch))
Effect of show=true with added Histogram, Waveform and
current_frame overlays:
LoadPlugin("waveform.dll") # or autoload
V = BlankClip(pixel_type="YUV444P8", width=480, height=360).Loop()
A = WavSource("music.wav")
AudioDub(V, A).AudioTrim(0.0, A.AudioDuration)
ScriptClip(Last, """Subtitle(Last, "frame "+String(current_frame), align=5)""")
Normalize(volume=1.0, show=true).Crop(0,0,-120,0).AddBorders(120,0,0,0)
Histogram(mode="audiolevels")
Waveform(window=3, under=true)
return Last
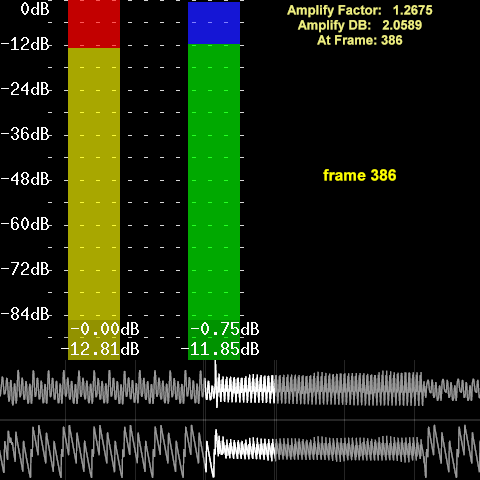
Showing frame 386 where the loudest peak was detected, but note that Amplify Factor is the same for all frames.¶
Changelog¶
Version |
Changes |
|---|---|
AviSynth 2.5.0 |
Replaced left and right parameters with |
AviSynth 2.0.8 |
Added |
AviSynth 2.0.3 |
Added Normalize filter. |
$Date: 2022/03/05 15:10:22 $